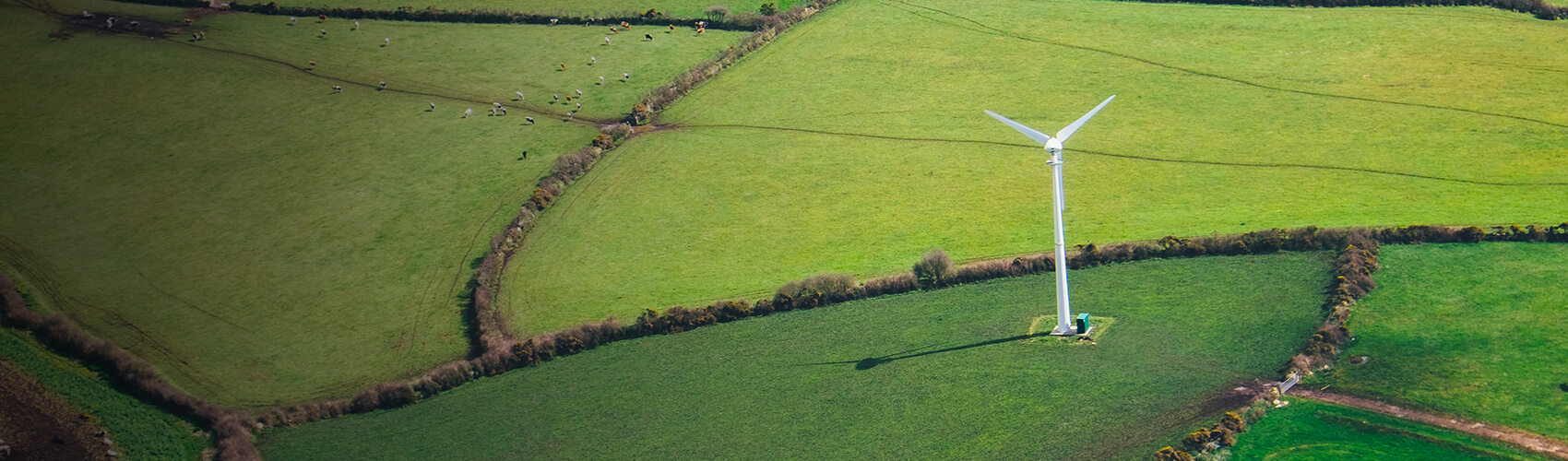
To meet its needs, humanity today consumes 1.8 times the resources that the planet can renew in a year and this ecological debt will double as a result of population and economic growth. The challenge for OCP Group is therefore to meet these growing consumption needs in order to guarantee food security while using a minimum of resources. The circular economy, making it possible to optimize the life cycle of products from their design to their end of life, including their production, use and reuse, is a top priority area in our commitment to sustainable production.
OCP Group's Circular Economy Program is structured around four major areas:
- Preservation of resources
- Sustainable production
- Smart consumption
- Value creation through transformation and recycling.
- Environment
- 1. Effluent
- 2. Emissions
- 3. Waste
- 4. Biodiversity
As part of its development policy, OCP Group launched a new industrial processing strategy in 2008, aimed at doubling its mining capacity and tripling its processing capacity. By doing so, OCP Group has made preserving natural water resources central to its concerns. The challenge is to use water efficiently and fulfill current and future water needs of its mining and industrial facilities.
OCP Group has taken the proactive decision to transition away from using water from conventional sources, deemed a national strategic resource for Morocco by 2030. OCP Group has developed an integrated and sustainable Water Program, making it possible to achieve industrial development objectives with two key areas of focus:
Optimized water use across the entire value chain;
The use of non-conventional water resources: treated (domestic) wastewater and desalinated seawater.
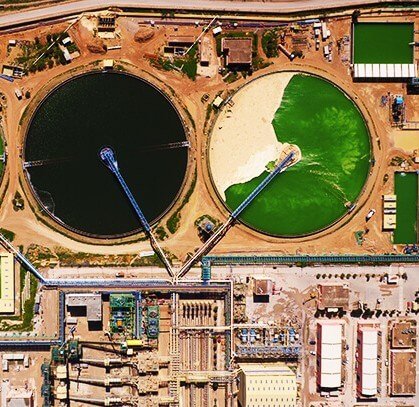
As part of its environmental excellence approach, the OCP Group uses all the human, technical and organizational means enabling it to operate within the standards’ threshold values for liquid discharges.
The OCP Group is therefore constantly compliant with the legal regulatory requirements and other voluntary ones in terms of liquid discharge ensuring the prevention and the control of environmental risks.
OCP Group's environmental footprint also includes air emissions from its industrial facilities. For years, OCP Group has been establishing environmental policies aimed at controlling its emissions and ensuring compliance with national regulations as well as adopting the best available technologies (BAT).
The Circular Economy vision OCP Group has adopted goes beyond regulatory compliance and develops true leadership to integrate into adjacent urban landscapes. To achieve this, OCP Group has relied on two main actions:
- The first is the massive investment to develop best-in-class technologies.
- The second aims to set up a state-of-the-art environmental management system to ensure complete management of its emissions.
Waste management is a key part of OCP Group’s circular economy strategy, integrating the regulatory aspect imposing the classification, identification and treatment of waste according to their type.
It is in this context that the waste program was launched, exploring the different waste recovery systems, and aiming for maximum value creation.
Aware of the issues that put pressures on biodiversity and acting as a responsible industrial player, OCP Group is committed to taking measures, controlling and compensating negative impacts on biodiversity.
The respect of biodiversity, the protection, the conservation and the responsible use of biologically diversified ecosystems are important aspects of our planning processes both at the mines and industrial units
In line with legal requirements, industrial development projects systematically undergo acceptability studies before being authorized. These include biodiversity considerations and respect for protected areas.

Aware of the climate change challenges , the impact it could have on its activities and anxious to participate actively in the objective of GHG emissions reduction defined by Morocco, OCP Group has led since 2008, as part of its industrial development program, a pioneering strategy for adapting to climate change and reducing its CO2 emissions along its value chain.
In addition, convinced that climate change constitutes a worldwide major systemic risk for food security, OCP Group works for resilient and sustainable agriculture, by aiming to transform these risks into opportunities to create value for the company and its ecosystem.

As part of its development policy, OCP Group launched a new industrial processing strategy in 2008, aimed at doubling its mining capacity and tripling its processing capacity. By doing so, OCP Group has made preserving natural water resources central to its concerns. The challenge is to use water efficiently and fulfill current and future water needs of its mining and industrial facilities.
OCP Group has taken the proactive decision to transition away from using water from conventional sources, deemed a national strategic resource for Morocco by 2030.
OCP Group has developed an integrated and sustainable Water Program, making it possible to achieve industrial development objectives with two key areas of focus:
- Optimized water use across the entire value chain;
- The use of non-conventional water resources: treated (domestic) wastewater and desalinated seawater.

Industrial processes inherently consume significant amounts of energy. Extraction and beneficiation activities account for 40% of total consumption, while processing accounts for 60%. OCP Group's growing industrial capacities, in line with the increase in fertilizer demand, implies an increasing need for electricity. In response to this situation, OCP Group has developed a responsible Energy Program with the goal of diversifying its energy mix and achieving self-sufficiency. The program is based on the following action plans:
- Development of cogeneration capacity
- Implementation of energy efficiency measures
- Increased use of renewable energy in the energy mix

The OCP Group, as a steward of the world's largest phosphate reserves has the responsibility to develop an industrial program that places the environmental and resource preservation at the center of its activity. The integration of these environmental challenges has led the company to set up the Circular Economy principles based on 4 different axes:
- Resource preservation,
- Sustainable production,
- Smart consumption
- And value creation through processing and recycling.
The Phosphate Stewardship is one of the main work stream of the OCP Group's Circular Economy program and represents the Group’s strong commitment to the sustainable management of the Phosphate resource.

The OCP group attaches significant importance to the rehabilitation of its mines by adopting international best practices while developing the economic attractiveness of the territory.
Mining has significant impacts on the soil, which is why OCP Group adopted new industrial processes for eco-friendly mine reclamation. This requires the recovery, storage, and reuse of topsoil during the planting phase of rehabilitation. All these phases involve agricultural experimentation through the planting of diverse trees and species, which benefits nearby communities

The new urban development Poles, the technopoles as well as the green cities that OCP Group initiates represent a model for sustainable development in several regions of the Kingdom, with the objective of a viable economic and social development, a guarantee of a pleasant living environment. and an attractive working and teaching environment, combined with an environment-friendly layout. This is how OCP Group launched four resolutely ecological projects:
- "The Green City Mohammed VI" in Benguerir which includes a university pole, "Mohammed VI Polytechnic University",
- The "Urban Pole of Mazagan" (PUMA) in the region of El Jadida, a real city at the confluence of knowledge and innovation,
- The "Green Mine" in Khouribga, a new urban and leisure center to enhance the city of Khouribga,
- And the "Foum El Oued Technopole", an innovation and R&D platform in the region of Laâyoune.
This approach is aligned with the following SDGs:

Read more
Our policies
Explore the policies we have in place to ensure we can make a significant difference for our environment, communities and business.
Our progress
Discover more about our wide-reaching sustainability progress in our latest reports and fact sheets.
Our customization process
Our customized fertilizers are radically improving yields and reducing environmental impact – helping farmers be greener and more efficient.